Product cost is a fundamental concept in product management and operations. It represents the total cost of producing a product, including materials, labor, and overheads. Understanding product cost is essential for setting prices, managing budgets, improving production efficiency, and making strategic decisions. Period costs, on the other hand, bookkeeping are not directly tied to producing a specific product. Instead, these costs are incurred as part of a company’s overall operations and are expensed in the period in which they are incurred.
Overhead Cost Calculation:
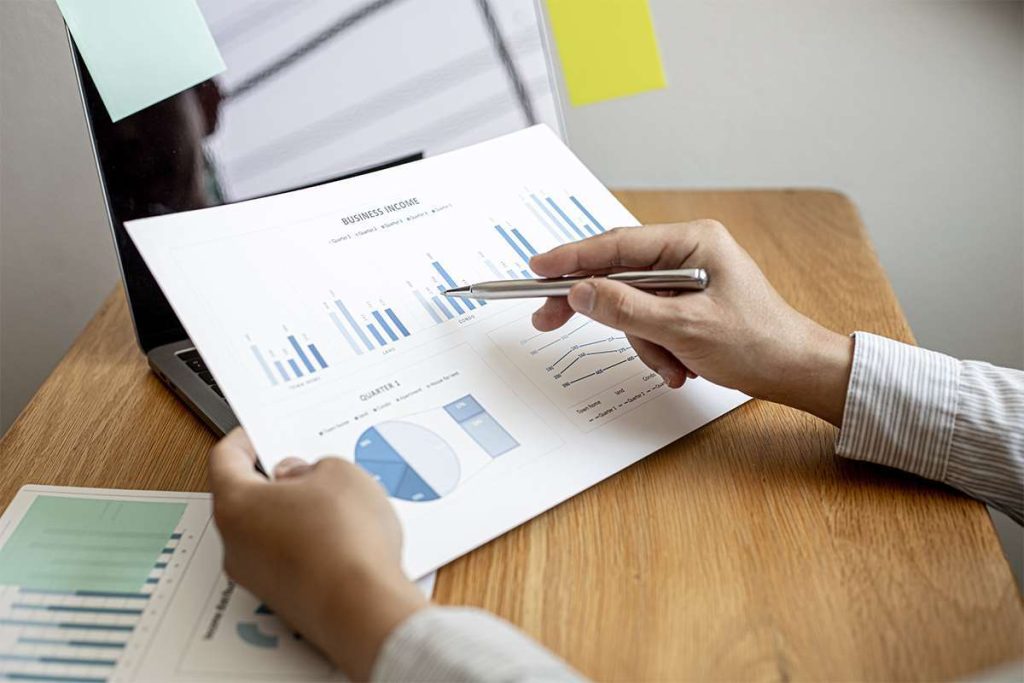

A thorough understanding of product costs allows businesses to create realistic budgets and develop accurate financial projections. With a clear picture of their costs, they product cost consist of can allocate resources effectively, make informed investment decisions, and plan for future growth and expansion. To keep things simple, production costs are expenses incurred when producing your product or service. Manufacturing costs, on the other hand, relate to only the expenses that are required to make your product or service. To determine the average cost, you simply divide the total cost of production by the total unit of output. Basically, it’s how much it costs you to produce a single product or service, or the cost per unit.
Direct labor
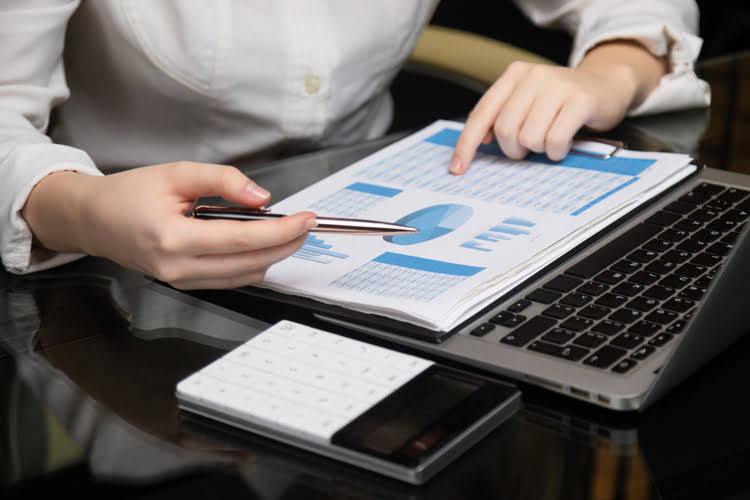

VSM is a process that helps identify areas where waste can be eliminated. This can be done through process analysis and improvement, better scheduling, and other methods. Costs incurred to produce a product intended to sell to a customer is called Product Costs. Before you even begin developing a product, you need law firm chart of accounts a clear plan for what you’re building. Without a project plan or product roadmap, it’s hard to make sure all stakeholders and teams are on the same page.
- If you are a company considering undercosting or overcosting your products, it is important to understand its potential consequences.
- It is a problem because they don’t have the right product costing strategy.
- For example, an in-house employee will expect benefits like paid time off, workspaces, and equipment.
- The number of units manufactured plays a significant role in determining the product cost.
- With a solid financial plan in place, you can identify which components are driving up your product costs and adjust accordingly.
- This does not include any indirect costs such as benefits or payroll taxes.
Pricing Strategy:
Understanding how to properly categorize these costs helps you optimize your spending, prioritize investments, and ultimately, drive the company’s growth and success. Selling and distribution expenses, administrative costs, research and development costs. In this article, we explore what constitutes product cost and how to calculate and manage it effectively. Firms can change the size of their production facility, adopt new technologies, and hire or lay off workers to optimize production. Keeping inventory for an extended period – whether completed goods or raw resources – may quickly add up. By considering all of these factors, you can get a reasonable estimate of the total cost of your product.
In the short run, some factors of production are fixed, while others are variable. Firms can only adjust the variable inputs (like labor and raw materials) to change the level of output, but cannot easily alter fixed factors (such as machinery or factory size). A cost function refers to the relationship between the cost of production and the level of output. It helps businesses calculate how much it will cost to produce different levels of output.
- For real-time knowledge of restaurant operations, a person should know the percentages of the food cost.
- If the product cost is higher than the industry average, it suggests that there may be inefficiencies in the production process that need to be addressed.
- Such materials, called indirect materials or supplies, are included in manufacturing overhead.
- Managers may also want to concentrate on a product’s impact on a bottleneck activity.
- Your accountant can also help you determine if any other parts of your business need to be looked at to avoid over-or under-costing.
- These costs are capitalized as inventory and become part of the cost of goods sold when the product is sold.