I teach so traders like you can have the opportunity an make a better future. I already explained how you can use them for trading, but long-term investors read and interpret them slightly differently. Fundamentals are often overlooked, but they can tell you a lot about a company over time. But it’s good to understand how it works and what it could mean. XYZ Company had the following figures extracted from its books of accounts. A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.
Resources
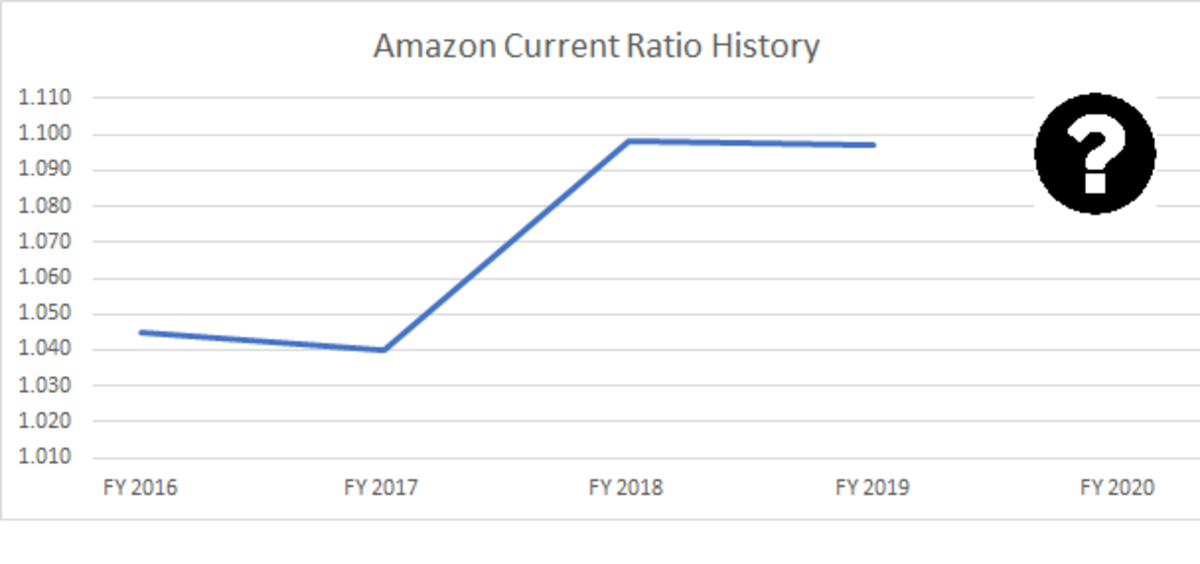
The current ratio can be a useful measure of a company’s short-term solvency when it is placed in the context of what has been historically normal for the company and its peer group. It also offers more insight when calculated repeatedly over several periods. Public companies don’t report their current ratio, though all the information needed to calculate the ratio is contained in the company’s financial statements.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Over-trading companies are likely to face substantial difficulties in meeting their day-to-day obligations. The current ratio can be expressed in any of the following three ways, but the most popular approach is to express it as a number.
Accounting Services
The current ratio measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months. Potential creditors use this ratio in determining whether or not to make short-term loans. The current ratio can also give a sense of the efficiency of a company’s operating cycle or its ability to turn how to track inventory in xero its product into cash. The formula to calculate the current ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities. In other words, the current ratio is a good indicator of your company’s ability to cover all of your pressing debt obligations with the cash and short-term assets you have on hand.
Start free ReadyRatios financial analysis now!
- The current ratio is used to evaluate a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations, such as accounts payable and wages.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
- These typically have a maturity period of one year or less, are bought and sold on a public stock exchange, and can usually be sold within three months on the market.
Combine the values of these items to determine the total current assets. Let’s say a business has $150,000 in current assets and $100,00 in current liabilities. The current ratio is $150,000 / $100,000, which is equal to 1.5. That means the company in question can pay its current liabilities one and a half times with its current assets. Putting the above together, the total current assets and total current liabilities each add up to $125m, so the current ratio is 1.0x as expected.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
He doesn’t want to rely on additional income that may or may not be generated by the expansion, so it’s important to be sure his current assets can handle the increased burden. Companies with a healthy current ratio are often viewed as being more creditworthy and better able to meet their short-term obligations. A current ratio of 1.5 means the company can pay its short-term debt off one and a half times with the current assets it has available. Generally, it is agreed that a current ratio of less than 1.0 may indicate insolvency. Sometimes, even though the current ratio is less than one, the company may still be able to meet its obligations.
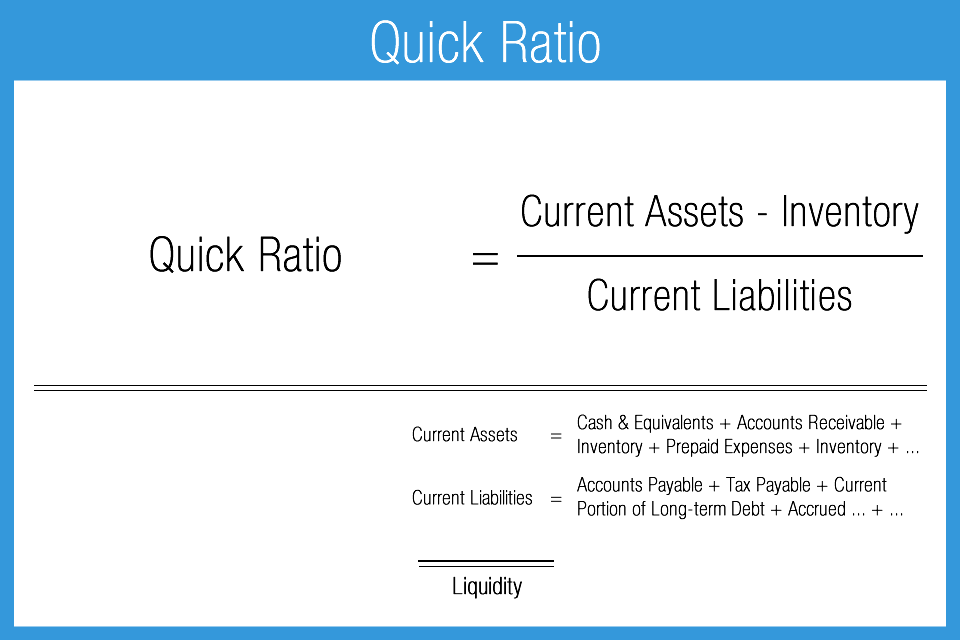
The quick ratio — aka the acid test — is another common liquidity ratio. Basically, the quick ratio takes out the least liquid current assets. Current ratio (also known as working capital ratio) is a popular tool to evaluate short-term solvency position of a business. Short-term solvency refers to the ability of a business to pay its short-term obligations when they become due. Short term obligations (also known as current liabilities) are the liabilities payable within a short period of time, usually one year.
Generally, prepaid expenses that will be used up within one year are initially reported on the balance sheet as a current asset. As the amount expires, the current asset is reduced and the amount of the reduction is reported as an expense on the income statement. These include cash and short-term securities that your business can quickly sell and convert into cash, like treasury bills, short-term government bonds, and money market funds. One limitation of the current ratio emerges when using it to compare different companies with one another. Businesses differ substantially among industries; comparing the current ratios of companies across different industries may not lead to productive insight. This could indicate that the company has better collections, faster inventory turnover, or simply a better ability to pay down its debt.
Such purchases require higher investments (generally financed by debt), increasing the current asset side. As of 2021, some industries tend to have higher current ratios than others, such as utilities and consumer staples. Conversely, industries such as technology and biotechnology tend to have lower current ratios.